I’ll never forget the first time I tried to buy concert tickets online. I was frantically typing in my card number and expiration date, my cursor hovering over the “Complete Purchase” button. Then, the site asked for my “CVV.” I froze. I flipped my card over and stared at the jumble of numbers, completely confused. Was it the last four digits of my card? The weird signature panel code? In a panic, I had to call my dad to ask, “What on earth is the CVV?” If you’ve ever been in that same stressful, pre-purchase moment, you’re in the right place. Let’s demystify this crucial little code together.
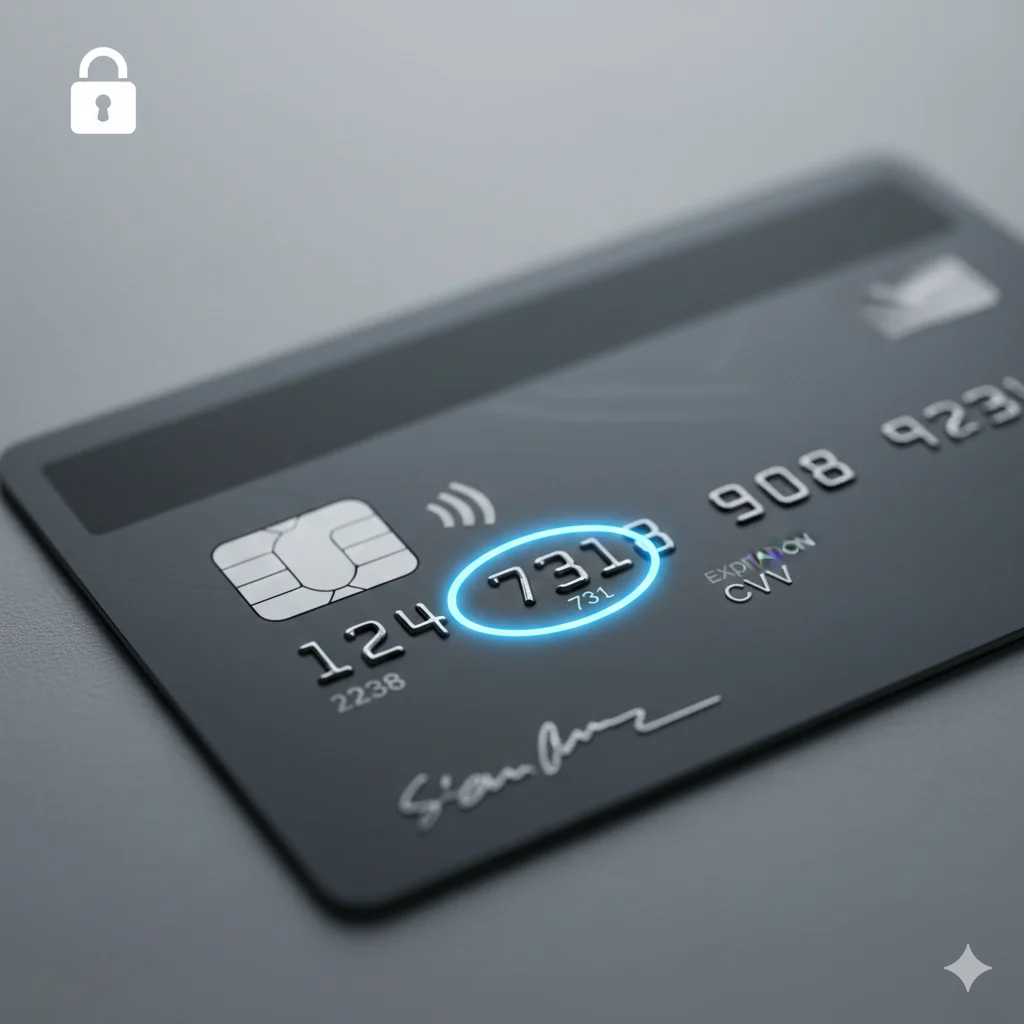
CVV means “Card Verification Value.” It’s a 3 or 4-digit security code on your credit or debit card designed to prove you have the physical card in your possession during “card-not-present” transactions, like online shopping.
🧠 What Does CVV Mean on a Credit Card?
Let’s get straight to the point. CVV is an acronym for “Card Verification Value.” Think of it as your credit card’s digital fingerprint or secret handshake. This unique code is a critical security feature engineered to protect you from fraud.
When you make a purchase online or over the phone where you can’t swipe your card’s magnetic stripe or insert its chip, the merchant has no way of knowing if you’re the legitimate cardholder. By asking for the CVV number, they are adding an extra layer of security. Because this code is (almost always) printed on the card itself and not stored in the magnetic stripe, it’s much harder for a thief who only has your stolen card number to use it for fraudulent online purchases.
In short: CVV = Card Verification Value = Your card’s secret security code for online purchases.
📱 Where Is Your CVV Code Located?
Finding your CVV is simple, but its location depends on the type of card you have. This is a primary point of confusion for many people, so let’s clear it up.
- For Visa®, Mastercard®, and Discover® cards: Your CVV is a 3-digit code located on the back of your card, printed on or just to the right of the signature panel.
- For American Express® cards: Your code, which Amex calls a CID (Card Identification Number), is a 4-digit code located on the front of your card, typically on the right side, just above your account number.
This code is not embossed like your card number, so it won’t be raised. It’s simply printed on the card, making it difficult for it to be captured if someone simply takes a photo of the front of your card.
💬 The Different Names for Your CVV Code
You might see this security feature called by a few different names. While they all refer to the same basic concept, the specific term often depends on the card network. Understanding these secondary terms is key to being a savvy cardholder.
- CVC (Card Verification Code): This is Mastercard’s term for it. It means the exact same thing as CVV.
- CID (Card Identification Number): This is the term American Express and Discover use for their 4-digit code on the front of the card.
- CSC (Card Security Code): This is a more generic term that encompasses all the others.
So, whether a site asks for your CVV, CVC, or CID, they’re all asking for that small, printed security code on your card. This is a fundamental part of credit card security and fraud prevention.
🛡️ Why is the CVV So Important for Security?
The CVV is a cornerstone of payment card security. Its primary purpose is to combat card-not-present (CNP) fraud, which is the most common type of credit card fraud today. Here’s how it works as a powerful anti-fraud measure:
- It Proves Physical Possession: When you provide the correct CVV, it strongly suggests that you have the genuine, physical card in your hand at the moment of the transaction.
- It’s Not Stored by Merchants: Due to strict PCI DSS (Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard) compliance rules, merchants are explicitly forbidden from storing your CVV after a transaction is authorized. Even if a hacker breaches a company’s database and steals your card number and expiration date, your CVV should not be there.
- It Adds a Critical Hurdle: For cybercriminals, not having the CVV makes using a stolen card number significantly more difficult. They might have the number from a skimmer or a data breach, but without the CVV, their ability to shop online is severely limited.
🔒 How to Keep Your CVV Safe
Protecting your CVV is just as important as protecting your card number. Following these secure online shopping practices will help you avoid financial scams and identity theft.
- Never Give It Out via Email or Text: Legitimate companies will never ask you to email or text a photo of your card or its CVV. This is a massive red flag for a phishing scam.
- Be Wary of Unsolicited Calls: If someone calls you claiming to be from your bank and asks for your CVV, hang up. It’s a scam. Your bank already has this information.
- Cover the Code in Public: When using your card at a terminal or ATM, consider covering the back of the card with your hand to prevent hidden cameras or prying eyes from capturing your CVV.
- Only Enter it on Secure Websites: Before typing your CVV, always ensure the website’s URL begins with
https://(the “s” stands for secure) and has a padlock icon in the address bar. - Consider a Virtual Card Number: Some banks and services like Privacy.com offer virtual card numbers. You can use a unique, randomly generated card number for each online merchant, which shields your actual card details, including the CVV.
🗣️ Real-Life Scenarios: When You’ll Need Your CVV
Let’s look at some practical, everyday situations where you’ll be prompted to provide your CVV code.
Online Retail Purchase:
- Website: “Please enter your payment information. Card Number: 4111 1111 1111 1111 | Expiry: 12/25 | Security Code: ___”
- You: Type in “123” (your 3-digit CVV) and complete the purchase.
Booking a Hotel or Flight:
- Travel Site: “To secure your reservation, we require your credit card details. Please provide the 3-digit code on the back of your card.”
- You: Find the code on the signature strip and enter it.
Phone Order with a Restaurant:
- Restaurant: “And for payment, I’ll need your card number, expiration, and the security code on the back.”
- You: Read the numbers, including the CVV, over the phone.
Setting Up a New Streaming Service:
- App: “Start your free trial. Enter your payment method. Don’t forget the CVV!”
- You: Input your card details and the CVV to activate the subscription.
✅ When to Use and When Not to Use Your CVV
Understanding the context for your CVV helps you spot fraudulent activity.
✅ When Providing Your CVV is Normal & Secure
- On encrypted e-commerce websites (
https://). - When making a legitimate phone order with a reputable company.
- For verifying your card with trusted payment gateways like PayPal or Stripe.
- When adding your card to a secure digital wallet (Apple Pay, Google Pay).
❌ When Providing Your CVV is a Major Red Flag
- In an unencrypted email or instant message.
- To someone who calls you unsolicited.
- On a website that does not have
https://in the URL. - To “verify your identity” in a suspicious pop-up ad.
- To a person claiming to be from the “IRS” or “Tech Support” who needs your card details.
CVV Usage Context Table
| Context | Example Phrase | Why It Works (or Doesn’t) |
|---|---|---|
| Online Shopping | Entering “123” in the CVV field on Amazon. | Secure & Standard: The site is encrypted, and the CVV is required to prove you have the card. |
| Phone Order | Telling a pizza place your card number, expiry, and CVV. | Generally Acceptable: The business is known and the transaction is immediate. |
| Reply to an Email | Emailing a photo of your card back to a “potential landlord.” | Dangerous & a Scam: CVV should never be transmitted via unsecured email. |
| In-Person Store | A cashier asks to see the back of your card for the CVV. | Unnecessary & Suspicious: In-person transactions use the chip or stripe, not the CVV. |
🔄 Other Card Security Features You Should Know
Your CVV isn’t the only security feature on your card. Modern payment technology uses a multi-layered approach to protect your finances and ensure secure transactions.
| Security Feature | What It Is | Its Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| EMV Chip | The small, metallic square on the front of your card. | Creates a unique transaction code for each purchase, making it nearly impossible to clone your card. |
| Magnetic Stripe | The black strip on the back of your card. | The older technology still used as a backup where chip readers aren’t available. |
| Contactless Payment | The symbol that looks like a wifi icon. | Uses NFC technology for quick, secure tap-to-pay transactions with dynamic encryption. |
| Address Verification Service (AVS) | A system that checks your billing address. | Verifies that the billing address you provide matches the one on file with your bank. |
❓ FAQs About CVV on a Credit Card
1. Is it safe to give out my CVV number?
It is only safe to give your CVV when making a transaction on a secure, encrypted website (look for https://) or over the phone to a verified, reputable business. Never give it out via email, text, or to someone who calls you unexpectedly.
2. What if my card doesn’t have a CVV?
All major modern credit and debit cards have a CVV/CID. If you genuinely cannot find it, your card may be damaged or worn out. In this case, you should contact your card issuer (e.g., your bank) to request a replacement card for security reasons.
3. Can someone use my card without the CVV?
While it is more difficult, it is not always impossible. Some older, less secure payment systems may not require a CVV. However, the vast majority of online merchants today will decline a transaction if the CVV is incorrect or missing, making it a vital layer of protection against fraud.
💎 Conclusion: Your Tiny Key to Big Security
That little three or four-digit CVV code on your credit card is a powerhouse of security. It’s your card’s personal bodyguard for the digital world, standing between your hard-earned money and potential fraudsters. Now that you know what CVV means on a credit card, where to find it, and how to protect it, you can shop online with greater confidence and awareness. Remember, it’s more than just a number—it’s a crucial tool in your financial safety toolkit. Guard it wisely, use it on secure sites, and you’ll be taking a major step toward mastering your own financial literacy and security. Happy and safe shopping

William Shakespeare was a legendary English playwright, poet, and storyteller whose works have shaped literature for centuries. Known for his timeless plays and sonnets, he continues to inspire writers, artists, and readers around the world with his mastery of language and storytelling.